Basics of Human Anatomy - Bones & Movements of the Human Body
By SCMA On 10/07/2017


For many medical assistants, remembering all the bones of the human body is a challenge. SCMA® provides a reviewer for medical assistants preparing for the Orthopedics Specialty Medical Assistant Examination.
This brief review is best when paired with attending SCMA's webinar, Basics of Anatomy and would be beneficial to those working in any surgical field.
The human body has two parts to the skeletal system.
- Axial System
- Appendicular System
The Axial Skeleton System includes 1
- Bones of the skull (facial and cranial bones)
- Ossicles (small bone found in the middle ear)
- Hyoid bone (of the throat)
- Vertebrae
- Rib cage (also called thoracic cage)
- Sternum
- The Skeletal System
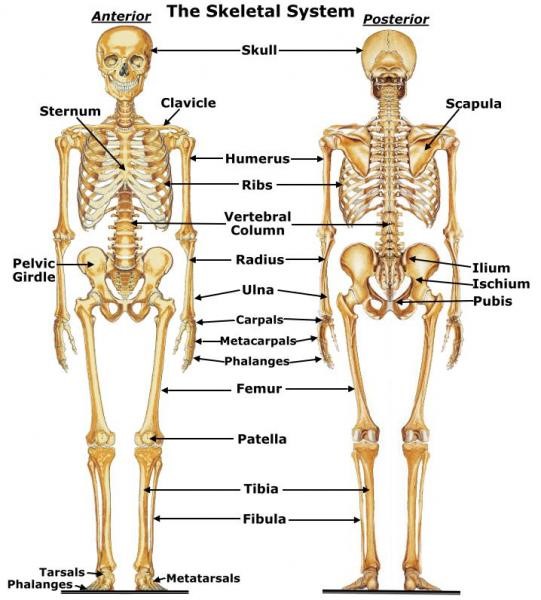
The Appendicular System includes the 1
- Pectoral girdles (clavicle and scapula)
- Arms and forearms (humerus, ulna, and radius)
- Hands (left and right carpals, metacarpals, proximal phalanges, intermediate phalanges, and distal phalanges)
- Pelvis (left and right hip bone)
- Thighs and legs (left and right femur, patella, tibia, and fibula)
- Feet and ankles (left and right tarsals, metatarsals, proximal phalanges, intermediate phalanges, and distal phalanges)
- The best way to describe the skeletal system is that our appendages i.e. arms and legs, hang off the axial system 2
Below is a list of movements including a brief description of each 3
- Flexion is the bending (decreasing) of the joint angle.
- Extension is the straightening (increasing) of the joint angle.
- Abduction entails moving away from the midline of the body.
- Adduction involves moving toward the midline of the body.
- Circumduction is the circular movement of a body part (of, for example, the hand, finger or a limb).
- Protraction is moving forward.
- Retraction is moving backward.
- Pronation is turning downward
- Supination is turning upward.
- Eversion is turning outward and
- Inversion is turning inward.
Need additional review for the Orthopedics Specialty Medical Assistant Examination?
Sign Up with us to get alerts on our free webinar on The Basics of Anatomy.
References
1.Vaughn, Phillip. Anatomy and Physiology: Anatomy and Physiology Made Easy: A Concise Learning Guide to Master the Fundamentals (Anatomy and Physiology, Human Anatomy, Human Physiology, Human Anatomy and Physiology) (pp. 101-102).
2. Kaplan. Medical Assistant Exam Strategies, Practice & Review with Practice Test (Kaplan Medical Assistant Exam Review) (p. 98). Kaplan Publishing.
3.Vaughn, Phillip. Anatomy and Physiology: Anatomy and Physiology Made Easy: A Concise Learning Guide to Master the Fundamentals (Anatomy and Physiology, Human Anatomy, Human Physiology, Human Anatomy and Physiology) (p. 93-100).
 844.885.1476
844.885.1476
